9 Vitamins for Eye Health
The eyes, being a sensory organ, play a crucial role in the functioning of the human body. Therefore, maintaining good eye health is essential for a person’s overall well-being and happiness. One way to ensure the health of this organ is to eat the right foods. Some foods have particular vitamins essential to enhancing one’s eyesight. Below are a few such vitamins that people should try to acquire for better vision.
Vitamin A
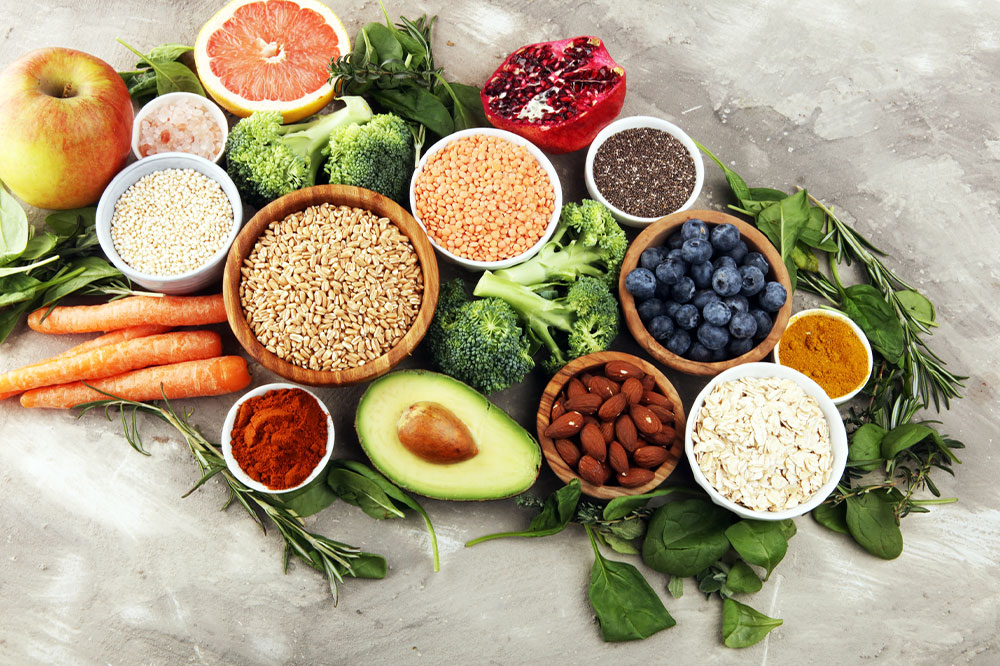
Regular consumption of vitamin A enables people to maintain a clear cornea—the outermost covering of the eyes. A healthy cornea improves vision and prevents irritation in the eyes. When broken down by the body, vitamin A turns into a protein called rhodopsin, which facilitates visibility in low-light conditions. Unsurprisingly, a deficiency of this vitamin is known to cause night blindness and, eventually, xerophthalmia. People with xerophthalmia initially suffer night blindness and, with progressively worsening symptoms, irreversible blindness. Due to these reasons, vitamin A is absolutely essential. This nutrient can be acquired from foods like butternut squash, sweet potatoes, and organ meats.
Beta-carotene
Beta-carotene is a pigmentation vitamin belonging to a family of chemical compounds called carotenoids. Carotenoids are common in carrots, tomatoes, and bell peppers. Interestingly, these foods also get their distinct, bright colors from carotenoids. Beta-carotene is essential to produce vitamin A in the body. In that sense, we can say that beta-carotene is not precisely a vitamin but a provitamin A carotenoid that the body converts into vitamin A. Beta-carotene is a potent antioxidant that prevents inflammation. Besides providing anti-inflammatory benefits, it lowers one’s risk of severe age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Vitamin C
Besides playing a part in strengthening the immune system, vitamin C boosts collagen synthesis. This, in turn, makes the connective tissues and blood vessels stronger in all body parts, especially the eyes. Vitamin C also promotes the health of a person’s eye lenses, which help focus on objects nearby or far away. Since there is no direct blood supply to the lenses, they receive nutrition from the fluid flowing in front of them. This fluid has approximately ten to 20 times more vitamin C than other body parts. All these reasons underline the sheer vitality of vitamin C in the body. A few foods rich in vitamin C are bell peppers, strawberries, and citrus fruits like oranges, kiwi, lemon, and grapefruit.
Lutein and zeaxanthin
Like beta-carotene, lutein and zeaxanthin belong to the carotenoid family of chemical compounds. They are great for eye health due to their ability to reduce the risk of macular degeneration. The chemical properties of these two carotenoids prevent eye damage caused by oxidative stress and blue light. Apart from preventing AMD, lutein and zeaxanthin help manage the symptoms of many skin conditions.
B-complex vitamins
Vitamins B6, B9, and B12 are three B-complex vitamins that specifically and very positively impact a person’s eye health. They reduce homocysteine, a protein that causes many undesirable health issues, including macular degeneration. Healthcare research studies have found that regular consumption of these vitamins—about 1,000 mcg of B12 coupled with B6 and B9—reduces the chances of macular damage and eventual degeneration in women. Therefore, vitamin B-rich foods like salmon and leafy greens must be a regular part of daily meals.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Many people are aware of the many benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health. But only a few know that these fatty acids are just as good for enhancing a person’s eye function. Omega-3s alleviate issues like dry eye disease. Therefore, numerous eye drops use this nutrient to treat the condition. Omega-3 fatty acids have also been scientifically found to reduce the risk of developing macular degeneration. One can find these healthy fats in abundant quantities in fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, and others), flaxseeds, walnuts, soybean, canola oils, and chia seeds.
Vitamin E
Oxidative stress is one of the most common reasons behind major eye disorders. It is a term used to describe an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Due to oxidative stress, free radicals can damage the eye cells. Vitamin E prevents this by protecting the eye cells from harmful and dangerous free radicals. Apart from this benefit, vitamin E has been found to reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related eye diseases. It is just as vital as vitamins A and C for healthy eyes. A few foods rich in vitamin E are sunflower seeds, almonds, avocados, and peanuts.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral with vitamin-like properties. It is an indispensable component of several enzymes that enhance a person’s vision and the integrity of eye cells and tissues. Zinc can reduce the risk of oxidative stress, protect the retina from free radicals and external elements, and help prevent age-related eye impairment. These capabilities make it crucial for people with AMD and those wanting to keep their eyes healthy. One can follow a meal plan rich in zinc to enjoy the benefits of this mineral. A few foods to consider are beans, lentils, seeds, meat, eggs, dairy products, and seafood.
Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin also belongs to the group of carotenoids. It is known to relax a person’s ciliary muscles, reducing the likelihood of developing strained eyes. Due to this benefit, astaxanthin can help revitalize the eyes after a busy day at work or a day filled with screen time. This vitamin also has incredible antioxidative properties, which means it restores the oxidative balance in the body by eliminating free radicals and facilitating a healthy flow of blood to and from an individual’s retina. Salmon, red trout, and krill are a few fish with high reserves of astaxanthin.
While these vitamins have several benefits for the eyes, one must consult their local healthcare expert before making extensive changes to their daily meals to avoid health complications.