Foods to Eat and Avoid With Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is an eye disease that affects the central portion of the retina, also called the macula. The macula is responsible for the sharpness of one’s central vision. Macular degeneration makes it difficult to perform everyday activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces. The disease has no cure, but its progression can be slowed. Before discussing the nutritional choices for macular degeneration, let us look at its symptoms and types.
What are the symptoms of macular degeneration?
The condition can lead to blurred or distorted vision, difficulty seeing in low light conditions, loss of central vision, difficulty recognizing faces, blank or dark spots in the central vision, and visual hallucinations in some cases. While anyone can develop these symptoms, macular degeneration is prevalent in people over 50. Since the disorder is more common with age, it is also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Besides seniors, people with a family history of AMD are likelier to develop the symptoms later in life. The disorder’s exact cause is unknown, but age, genetics, lifestyle, and food habits are some risk factors.
What are the types of macular degeneration?
AMD is broadly classified into two types:
Dry macular degeneration
This condition occurs when the cells in the macular break down, and the macular gets thinner with age. It is more common and can be detected at an early stage. With treatment and a good lifestyle, the remaining vision of an individual can be preserved and protected.
Wet macular degeneration
This type is more severe and is characterized by the growth of abnormal blood vessels beneath the macula. It is usually a late-stage condition that develops rapidly and may lead to blindness if left untreated.
What to eat for macular degeneration?
Healthy food habits can help lower macular degeneration risk and slow its progression. The following foods are rich in nutrients essential for eye health:
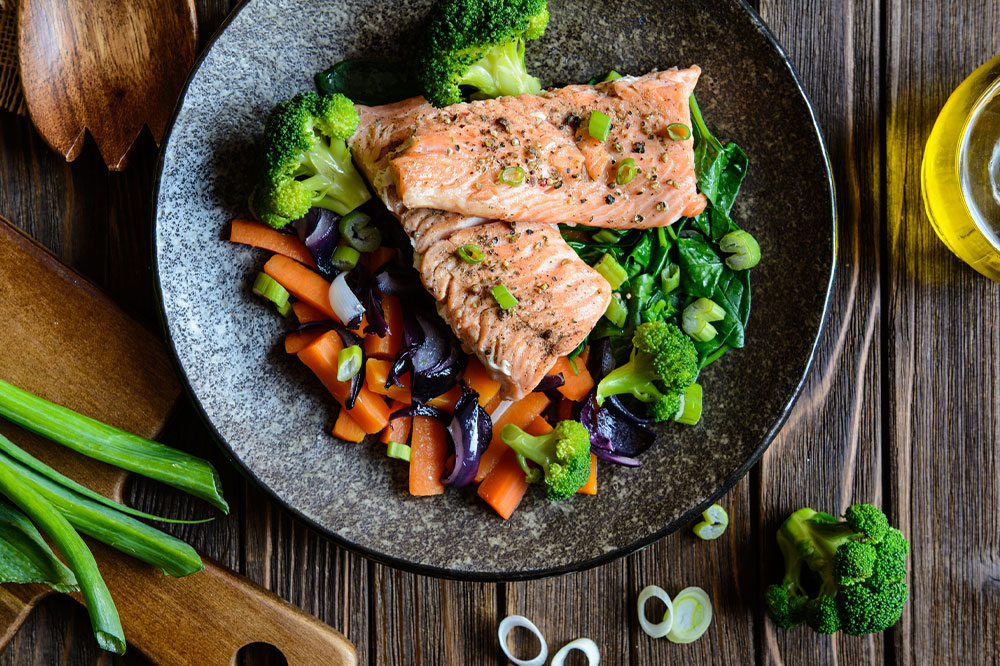
Fish
Fish is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce eye inflammation. Salmon, mackerel, tuna, anchovies, and sardines are all good choices.
Whole grains
Whole grains like oats, bulgur, sorghum, quinoa, millet, whole wheat, and brown rice are rich in fiber. These foods help pull out the excess cholesterol from the body and reduce the risk of AMD.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds like almonds, cashews, walnuts, Brazil nuts, and flax and sunflower seeds are good sources of vitamin E, an antioxidant that helps protect the eyes from damage.
Citrus fruits
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are high in vitamin C, an antioxidant that can help boost eye health.
Vegetables
Dark, leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that help protect the macula from damage. Some other veggies that protect cells from oxidative damage include broccoli, pumpkin, Brussels sprouts, corn, peas, and green peppers.
Carrots
Carrots are abundant in beta-carotene, a compound the body converts into vitamin A. Vitamin A is an essential nutrient for good vision, and its deficiency can lead to macular degeneration.
Eggs
Eggs are a good source of lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that help protect the macula from damage.
What to avoid with macular degeneration?
While the above foods support eye health, a few have the opposite effect and should be avoided. Examples are:
Processed foods
Processed foods high in trans fats, sugar, and salt can contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. These factors can damage the cells in the retina and contribute to the development of AMD.
Saturated and trans fats
Saturated and trans fats are found in fried foods; processed snacks like chips, fried chicken, cookies, and pretzels; and fatty meats like bacon, red meat, and sausages. These fats can contribute to inflammation in the body, which can lead to macular degeneration.
High-glycemic index foods
High-glycemic index foods like white bread, pasta, and sugary drinks can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This can contribute to inflammation in the body, leading to macular degeneration.
Caffeine
Beverages like tea and coffee have caffeine, which can interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients essential for eye health.
What are the other ways to deal with AMD?
Here are some other ways one can reduce the risk of macular degeneration:
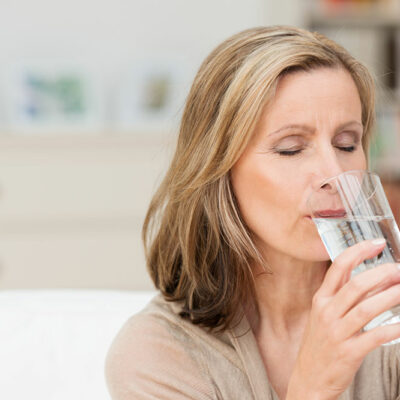
Hydration
Drinking plenty of water can help keep the eyes hydrated and prevent dryness that may exacerbate AMD symptoms.
Eye protection
Wearing sunglasses and a hat can protect the eyes from harmful UV sun rays and reduce the risk of AMD.
Physical activity
Regular exercise can improve blood flow to the optic nerve and retina. Besides workouts, simple activities like blinking more often and shifting focus between near and far objects can enhance eye health.
Managing cholesterol
High levels of bad cholesterol can lead to the buildup of fatty deposits in the blood vessels, including those in the eyes. This buildup can reduce blood flow to the eyes, increase inflammation, and affect the delicate blood vessels, which can contribute to impaired vision.
Eye check-ups
Regular eye check-ups can help detect AMD early and prevent vision loss. One should have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once every two years or more frequently if they have a higher risk for AMD or after age 40.
In severe cases, a vision specialist may recommend treatments besides lifestyle changes to help patients make the most of their remaining eyesight. The professional can also provide advice on surgeries that could stop the illness at an early stage. One of the common therapies is anti-VEGF, which aims to stop the growth of abnormal blood vessels to prevent vision loss. Photodynamic therapy aims to destroy abnormal blood vessels in the eye; it uses a laser for the purpose, and the process may be repeated every few months. The treatment can also seal leaking blood vessels in the eye. Besides surgery, a doctor may recommend high doses of specific vitamins and minerals to slow down the progression of macular degeneration in some people.