Headache – Symptoms, Triggers, and Management
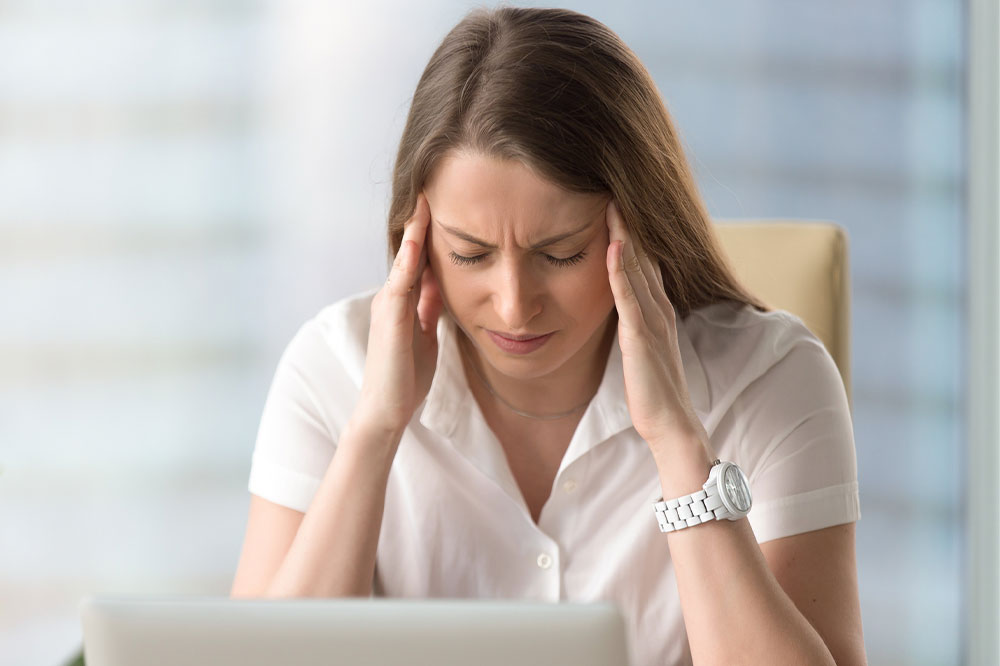
Headache is one of the most common types of pain. It can affect anyone at any age. Headache is often a primary problem and not a symptom stemming from an underlying condition. Migraine is one of the types of headache condition that affect many people. A migraine attack can continue for hours or even days, and the pain is unbearable, making it challenging to go about daily activities. Here are common headache signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
4 signs of headaches
Thunderclap headache
A “thunderclap” headache is a sudden, severe headache that peaks in intensity within 60 seconds of beginning. Even though the headache quickly improves, this is a dangerous sign that shouldn’t be ignored. A thunderclap headache, also known as cerebral hemorrhage, can be caused by an aneurysm, a stroke, or a head injury. This headache type requires immediate medical attention as it can be detrimental to one’s health.
Headache followed by a stiff neck and a high fever
Meningitis is a severe condition characterized by a headache, stiff neck, high fever, and neurological symptoms such as convulsions. This illness is caused by swelling of the membranes surrounding the spinal cord and brain, which can be caused by a viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection. Never ignore a headache with a stiff neck because meningitis necessitates immediate medical attention. Bacterial meningitis can be fatal, so prompt antibiotic treatment is necessary.
Temple tenderness or pain
Individuals over 50 who experience a pounding headache in the temple area may have giant cell arteritis, also known as temporal arteritis, in which the blood vessels in the head are inflamed. Other signs and symptoms include headaches, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, visual abnormalities, and jaw pain or difficulty chewing. The condition affects women more frequently than it affects men. A sudden vision loss could happen if the illness is not identified in time.
Eye redness with headache
In addition to headache, other glaucoma symptoms include eye pressure, blurred vision, red eyes, and the appearance of colored halo rings around lights. If glaucoma is not treated, it can cause permanent blindness. Sometimes, these symptoms can progressively worsen; other times, eye pressure, a severe headache, and eye pain may suddenly spike. In such a situation, dial 911 or arrange patient transportation to the emergency room.
A migraine is the most common headache; it frequently begins as a dull pain before becoming excruciatingly painful. Migraines can also be frequently induced after physical activity. The pain could be in the forehead or moving from one side to the other. Approximately half of the patients vomit, and about 80% also experience nausea and headaches. A migraine attack typically lasts 4 hours, but the worst cases can last up to 3 days. Some people only occasionally experience migraines, whereas others do so once or twice a year.
Triggers of migraine
Migraines can be brought on by various things, including changes in a woman’s hormone levels. When estrogen levels fluctuate, such as during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, many women appear to suffer from headaches. Some drinks, such as soft drinks with caffeine, stress, or bright or flashing lights, can also cause migraines. Some people can get migraines when exposed to strong scents like perfume, paint thinner, etc. Additionally, processed foods, salty meals, and aged cheeses can cause migraines.
Migraine relief techniques
Migraine treatment is meant to reduce symptoms and prevent future episodes. Several drugs are effective in treating migraines. There are primarily two types of medications used to treat migraines: Painkillers can be given to reduce pain and other symptoms when a migraine episode occurs. Regular use of preventive medications can lessen the intensity or frequency of migraines. The frequency and intensity of headaches, nausea, vomiting, and other medical issues determine the preferred course of treatment. When the migraine symptoms begin, try entering a silent, dark room. At the first sign of a headache, close your eyes and get some rest or a nap. Drink a lot of water and apply a cool compress or ice pack wrapped in a towel or cloth to the forehead.
Home remedies for migraine
Food changes
Food is critical to migraine prevention. Many foods and beverages can cause migraines, including deli meats, chocolate, cold foods like ice cream and iced drinks, processed foods, pickled foods, hot dogs, and ice cream. Caffeine may help relieve migraine symptoms in some people. Keep a daily food log to identify the foods that trigger migraine attacks. Eliminate foods that cause severe headache symptoms. This will result in fewer headaches.
Essential oils
A lavender essential oil may help relieve stress, anxiety, and headaches. They include basil, chamomile, peppermint, and lavender. Topically applied basil oil reduces the duration and frequency of migraine episodes. It is important to note that some essential oils may harm children. Individuals should only use a diffuser to inhale essential oils. Always dilute any topical application with a safe concentration of carrier oil. Please seek medical advice before using any new item on the body.
Massage
Massage the shoulders and neck muscles to relieve stress and migraine pain. Massage can also help reduce stress. A professional massage may be beneficial to eliminate the pain. Roll a clean tennis ball along the shoulders and back while leaning against a wall to relieve pain and get immediate relief.
Eat regularly
A typical migraine episode is triggered by skipping meals or waiting too long between them. A headache may also result from low blood sugar brought on by fasting. Get into the habit of always having water on hand to drink, especially during activity, as even mild to moderate dehydration can cause a migraine attack or headache.
Ice packs
Although ice and heat can reduce discomfort, most migraine patients prefer a cold compress. Cold packs can be applied to the neck, forehead, and temples. The skin should always be protected from ice packs by a towel. Check for leaks before using a commercial cold pack to ensure no chemicals can escape and harm the eyes.