Nutritional choices to manage macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is an age-related disorder that affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for straight-ahead vision. The condition usually occurs when fluid from abnormal blood vessels leaks into the macula. Patients experience blurry vision and find it hard to read or drive. While the eye disorder has no cure, one can manage it effectively to lead a normal life. The following are the foods to eat and avoid with macular degeneration:
Foods to eat
Those with this eye disorder should add the following foods to their meals:
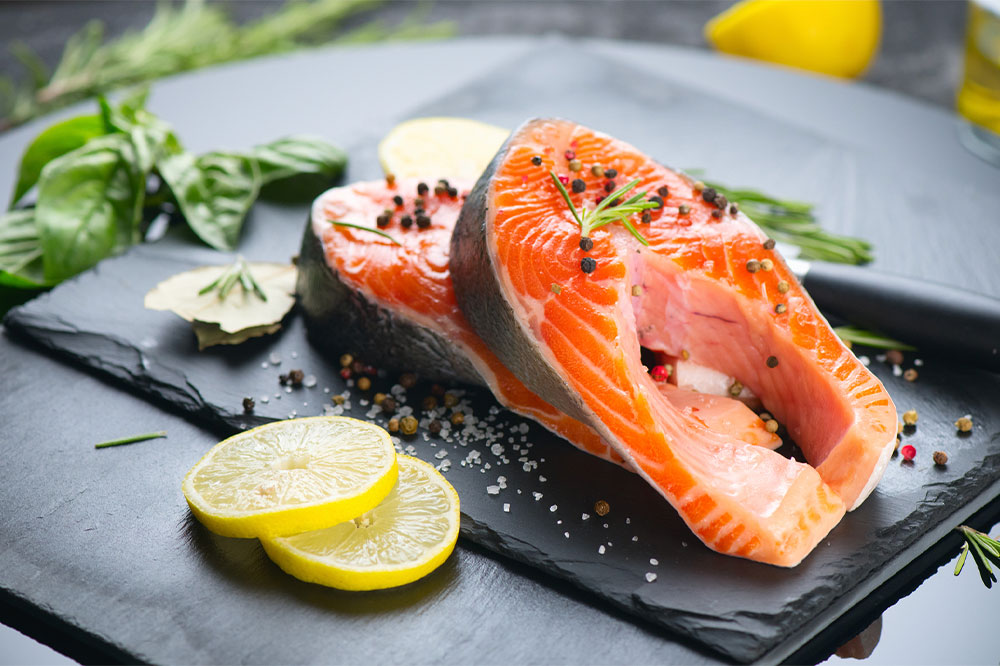
- Fatty fish
Fish is one of the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Several research studies have shown that these acids help manage the symptoms and even prevent the disease to a certain extent. Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, sardines, anchovies, and mackerel. - Spinach
This potent green leafy vegetable is abundant in natural compounds like zeaxanthin and lutein. These compounds not just prevent and delay the progression of macular degeneration but also safeguard against cataracts. Since the body needs fat to absorb these compounds, one can drizzle some olive oil (unsaturated fat) over spinach. - Almonds
Al monds are not just a delicious and filling snack but an effective food option to correct the effects of macular degeneration. They are rich in vitamin E, which prevents unstable molecules from attacking healthy eye tissues, ensuring their optimized functioning. Patients should aim for a quarter cup of almonds daily for maximum benefits. - Oranges
Researchers have found that a single serving of oranges every day prevents the risk of late macular degeneration by almost 60 percent around 15 years later. Flavonoids in oranges are the main compounds that help fight this condition. - Eggs
Eggs are a great source of lutein and zeaxanthin. These two compounds are directly responsible for significantly reducing the risk of macular degeneration. This is especially true for late-stage macular degeneration. - Chickpeas
Legumes are rich in zinc, which helps lower the risk of developing several eye conditions, including cataracts. Zinc contributes to the health of the retina and also improves night vision. - Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes are abundant in several healthy antioxidant compounds that get converted to vitamin A when digested in the body. This vitamin keeps the retina healthy and prevents its degeneration.
Foods to avoid
Individuals dealing with this health condition should avoid the following foods:
- Processed foods
Processed foods are rich in trans fats, which clog the vessels of the heart. They also pose a danger to the tiny blood vessels in the eyes. Examples of processed foods are pretzels, crackers, chips, and cookies. - Refined carbs
Foods rich in carbohydrates have a higher glycemic index. This means they can raise blood glucose levels quickly after a meal. Studies show that high-GI foods are associated with the onset of this eye disorder. So, pizzas, bagels, white bread, rice, and pasta are best avoided. - Butter and palm oil
The retina is made up of fatty acids, so naturally, fats can help keep it healthy. However, one must choose the right kind of fatty acids. Refined vegetable oils, butter, and refined oils are high in saturated fats, which increase the production of a harmful compound in the body. It, in turn, increases inflammation in the eye tissues, advancing the onset of macular degeneration. - Sweets
Excess sugar and starch intake is one of the leading causes of macular degeneration. Sugars increase the production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These compounds promote inflammation in the body and may lead to this eye disorder. - High-fat meats
The inflammation caused by fatty meats leads to oxidative stress in the eyes, which worsens the symptoms of this eye disorder. It also increases cholesterol levels, which can cause the thickening of eye blood vessels.
Proper nutrition can help with macular degeneration correction to a certain extent. But the patient may also need treatment. The popular options are:
- Bevacizumab (Avastin)
It is used for a particular type of this disorder called wet age-related macular degeneration (wet AMD). Bevacizumab (Avastin) helps slow the progression by blocking the VEGF protein that causes this condition. The common side effects are loss of appetite and constipation. - Ranibizumab (LUCENTIS)
It c an be used for wet AMD and other eye conditions. A health professional administers ranibizumab (LUCENTIS) directly into the eye, usually once a month. The treatment works by blocking a protein in the eye called VEGF, which is responsible for vision loss. It also prevents the growth of new abnormal blood vessels. Eye pain and eye irritation are some of the possible side effects. - Aflibercept (EYLEA)
T his is another option for wet AMD administered directly into the eye. Aflibercept (EYLEA) works by blocking the harmful protein, VEGF, often responsible for blurry vision. It can have side effects like watery eyes and eyelid swelling. One can contact a doctor to determine the dosing as per their need. - Brolucizumab (BEOVU and Novartis)
T his is a popular treatment for wet AMD, neovascular wet AMD, and diabetic macular edema. Brolucizumab (BEOVU and Novartis) is administered directly into the eyes and works by blocking a protein responsible for forming abnormal blood vessels. The side effects reported with this option are eye pain and vitreous floaters.